Publications
An up-to-date list is available on Google Scholar.
journal articles
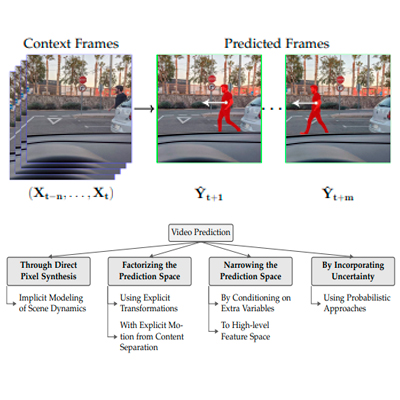 A Review on Deep Learning Techniques for Video PredictionOprea, Sergiu, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Castro-Vargas, John Alejandro, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, and Argyros, AntonisIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2020
A Review on Deep Learning Techniques for Video PredictionOprea, Sergiu, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Castro-Vargas, John Alejandro, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, and Argyros, AntonisIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2020The ability to predict, anticipate and reason about future outcomes is a key component of intelligent decision-making systems. In light of the success of deep learning in computer vision, deep-learning-based video prediction emerged as a promising research direction. Defined as a self-supervised learning task, video prediction represents a suitable framework for representation learning, as it demonstrated potential capabilities for extracting meaningful representations of the underlying patterns in natural videos. Motivated by the increasing interest in this task, we provide a review on the deep learning methods for prediction in video sequences. We firstly define the video prediction fundamentals, as well as mandatory background concepts and the most used datasets. Next, we carefully analyze existing video prediction models organized according to a proposed taxonomy, highlighting their contributions and their significance in the field. The summary of the datasets and methods is accompanied with experimental results that facilitate the assessment of the state of the art on a quantitative basis. The paper is summarized by drawing some general conclusions, identifying open research challenges and by pointing out future research directions.
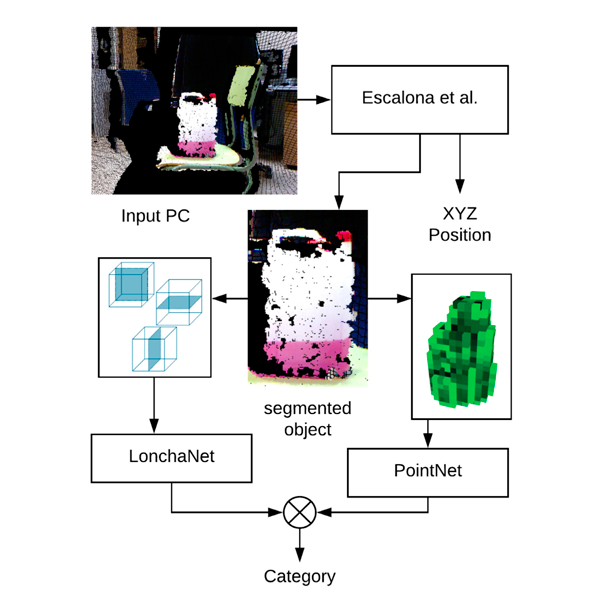 COMBAHO: A deep learning system for integrating brain injury patients in societyGarcia-Rodriguez, Jose, Gomez-Donoso, Francisco, Oprea, Sergiu, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Cazorla, Miguel, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Bauer, Zuria, Castro-Vargas, John, Escalona, Felix, Ivorra-Piqueres, David, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Aguirre, Eugenio, Garcia-Silviente, Miguel, Garcia-Perez, Marcelo, M.-Canas, Jose, Martin-Rico, Francisco, Gines, Jonathan, and Rivas-Montero, FranciscoPattern Recognition Letters 2020
COMBAHO: A deep learning system for integrating brain injury patients in societyGarcia-Rodriguez, Jose, Gomez-Donoso, Francisco, Oprea, Sergiu, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Cazorla, Miguel, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Bauer, Zuria, Castro-Vargas, John, Escalona, Felix, Ivorra-Piqueres, David, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Aguirre, Eugenio, Garcia-Silviente, Miguel, Garcia-Perez, Marcelo, M.-Canas, Jose, Martin-Rico, Francisco, Gines, Jonathan, and Rivas-Montero, FranciscoPattern Recognition Letters 2020In the last years, the care of dependent people, either by disease, accident, disability, or age, is one of the current priority research topics in developed countries. Moreover, such care is intended to be at patients home, in order to minimize the cost of therapies. Patients rehabilitation will be fulfilled when their integration in society is achieved, either in the family or in a work environment. To address this challenge, we propose the development and evaluation of an assistant for people with acquired brain injury or dependents. This assistant is twofold: in the patient’s home is based on the design and use of an intelligent environment with abilities to monitor and active learning, combined with an autonomous social robot for interactive assistance and stimulation. On the other hand, it is complemented with an outdoor assistant, to help patients under disorientation or complex situations. This involves the integration of several existing technologies and provides solutions to a variety of technological challenges. Deep leaning-based techniques are proposed as core technology to solve these problems.
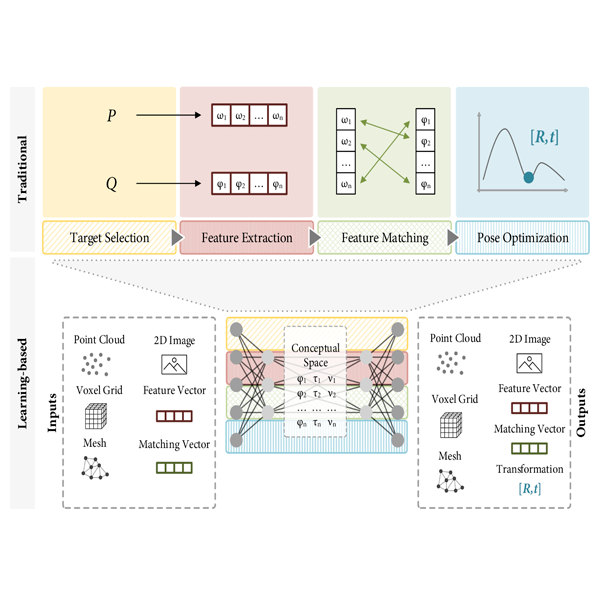 When Deep Learning Meets Data Alignment: A Review on Deep Registration Networks (DRNs)Villena-Martinez, Victor, Oprea, Sergiu, Saval-Calvo, Marcelo, Azorin-Lopez, Jorge, Fuster-Guillo, Andres, and Fisher, Robert B.Applied Sciences 2020
When Deep Learning Meets Data Alignment: A Review on Deep Registration Networks (DRNs)Villena-Martinez, Victor, Oprea, Sergiu, Saval-Calvo, Marcelo, Azorin-Lopez, Jorge, Fuster-Guillo, Andres, and Fisher, Robert B.Applied Sciences 2020This paper reviews recent deep learning-based registration methods. Registration is the process that computes the transformation that aligns datasets, and the accuracy of the result depends on multiple factors. The most significant factors are the size of input data; the presence of noise, outliers and occlusions; the quality of the extracted features; real-time requirements; and the type of transformation, especially those defined by multiple parameters, such as non-rigid deformations. Deep Registration Networks (DRNs) are those architectures trying to solve the alignment task using a learning algorithm. In this review, we classify these methods according to a proposed framework based on the traditional registration pipeline. This pipeline consists of four steps: target selection, feature extraction, feature matching, and transform computation for the alignment. This new paradigm introduces a higher-level understanding of registration, which makes explicit the challenging problems of traditional approaches. The main contribution of this work is to provide a comprehensive starting point to address registration problems from a learning-based perspective and to understand the new range of possibilities.
 UnrealROX: an extremely photorealistic virtual reality environment for robotics simulations and synthetic data generationMartinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Oprea, Sergiu, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Jover-Alvarez, Alvaro, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, and Garcia-Rodriguez, JoseVirtual Reality 2019
UnrealROX: an extremely photorealistic virtual reality environment for robotics simulations and synthetic data generationMartinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Oprea, Sergiu, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Jover-Alvarez, Alvaro, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, and Garcia-Rodriguez, JoseVirtual Reality 2019Data-driven algorithms have surpassed traditional techniques in almost every aspect in robotic vision problems. Such algorithms need vast amounts of quality data to be able to work properly after their training process. Gathering and annotating that sheer amount of data in the real world is a time-consuming and error-prone task. These problems limit scale and quality. Synthetic data generation has become increasingly popular since it is faster to generate and automatic to annotate. However, most of the current datasets and environments lack realism, interactions, and details from the real world. UnrealROX is an environment built over Unreal Engine 4 which aims to reduce that reality gap by leveraging hyperrealistic indoor scenes that are explored by robot agents which also interact with objects in a visually realistic manner in that simulated world. Photorealistic scenes and robots are rendered by Unreal Engine into a virtual reality headset which captures gaze so that a human operator can move the robot and use controllers for the robotic hands; scene information is dumped on a per-frame basis so that it can be reproduced offline to generate raw data and ground truth annotations. This virtual reality environment enables robotic vision researchers to generate realistic and visually plausible data with full ground truth for a wide variety of problems such as class and instance semantic segmentation, object detection, depth estimation, visual grasping, and navigation.
 A visually realistic grasping system for object manipulation and interaction in virtual reality environmentsOprea, Sergiu, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Castro-Vargas, John A., Orts-Escolano, Sergio, and Garcia-Rodriguez, JoseComputers & Graphics 2019
A visually realistic grasping system for object manipulation and interaction in virtual reality environmentsOprea, Sergiu, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Castro-Vargas, John A., Orts-Escolano, Sergio, and Garcia-Rodriguez, JoseComputers & Graphics 2019Interaction in virtual reality (VR) environments (e.g. grasping and manipulating virtual objects) is essential to ensure a pleasant and immersive experience. In this work, we propose a visually realistic, flexible and robust grasping system that enables real-time interactions in virtual environments. Resulting grasps are visually realistic because hand is automatically fitted to the object shape from a position and orientation determined by the user using the VR handheld controllers (e.g. Oculus Touch motion controllers). Our approach is flexible because it can be adapted to different hand meshes (e.g. human or robotic hands) and it is also easily customizable. Moreover, it enables interaction with different objects regardless their geometries. In order to validate our proposal, an exhaustive qualitative and quantitative performance analysis has been carried out. On one hand, qualitative evaluation was used in the assessment of abstract aspects, such as motor control, finger movement realism, and interaction realism. On the other hand, for the quantitative evaluation a novel metric has been proposed to visually analyze the performed grips. Performance analysis results indicate that previous experience with our grasping system is not a prerequisite for an enjoyable, natural and intuitive VR interaction experience.
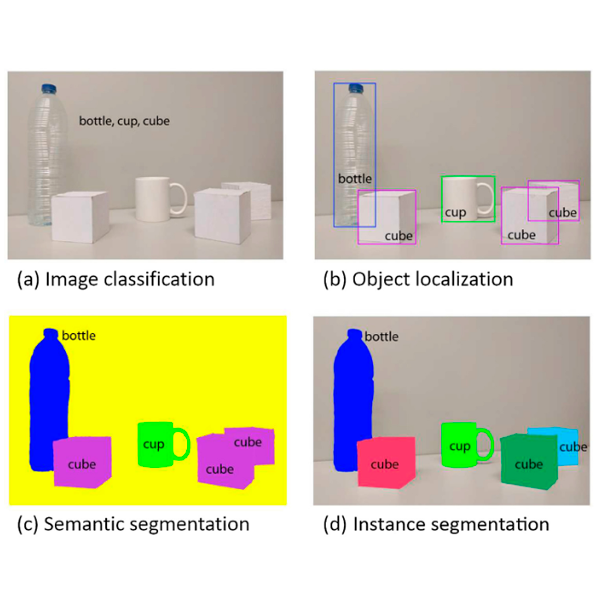 A survey on deep learning techniques for image and video semantic segmentationGarcia-Garcia, Alberto, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Oprea, Sergiu, Villena-Martinez, Victor, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, and Garcia-Rodriguez, JoseApplied Soft Computing 2018
A survey on deep learning techniques for image and video semantic segmentationGarcia-Garcia, Alberto, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Oprea, Sergiu, Villena-Martinez, Victor, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, and Garcia-Rodriguez, JoseApplied Soft Computing 2018Image semantic segmentation is more and more being of interest for computer vision and machine learning researchers. Many applications on the rise need accurate and efficient segmentation mechanisms: autonomous driving, indoor navigation, and even virtual or augmented reality systems to name a few. This demand coincides with the rise of deep learning approaches in almost every field or application target related to computer vision, including semantic segmentation or scene understanding. This paper provides a review on deep learning methods for semantic segmentation applied to various application areas. Firstly, we formulate the semantic segmentation problem and define the terminology of this field as well as interesting background concepts. Next, the main datasets and challenges are exposed to help researchers decide which are the ones that best suit their needs and goals. Then, existing methods are reviewed, highlighting their contributions and their significance in the field. We also devote a part of the paper to review common loss functions and error metrics for this problem. Finally, quantitative results are given for the described methods and the datasets in which they were evaluated, following up with a discussion of the results. At last, we point out a set of promising future works and draw our own conclusions about the state of the art of semantic segmentation using deep learning techniques.
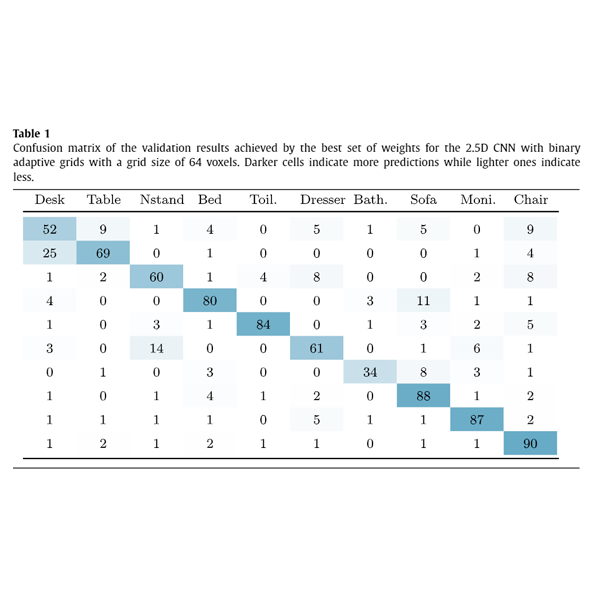 A study of the effect of noise and occlusion on the accuracy of convolutional neural networks applied to 3D object recognitionGarcia-Garcia, Alberto, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Oprea, Sergiu, Gomez-Donoso, Francisco, and Cazorla, MiguelComputer Vision and Image Understanding 2017
A study of the effect of noise and occlusion on the accuracy of convolutional neural networks applied to 3D object recognitionGarcia-Garcia, Alberto, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Oprea, Sergiu, Gomez-Donoso, Francisco, and Cazorla, MiguelComputer Vision and Image Understanding 2017In this work, we carry out a study of the effect of adverse conditions, which characterize real-world scenes, on the accuracy of a Convolutional Neural Network applied to 3D object class recognition. Firstly, we discuss possible ways of representing 3D data to feed the network. In addition, we propose a set of representations to be tested. Those representations consist of a grid-like structure (fixed and adaptive) and a measure for the occupancy of each cell of the grid (binary and normalized point density). After that, we propose and implement a Convolutional Neural Network for 3D object recognition using Caffe. At last, we carry out an in-depth study of the performance of the network over a 3D CAD model dataset, the Princeton ModelNet project, synthetically simulating occlusions and noise models featured by common RGB-D sensors. The results show that the volumetric representations for 3D data play a key role on the recognition process and Convolutional Neural Network can be considerably robust to noise and occlusions if a proper representation is chosen.
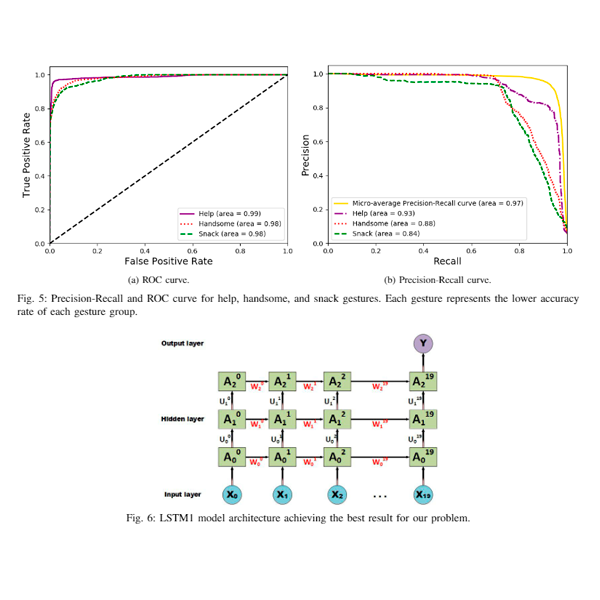 A long short-term memory based Schaeffer gesture recognition systemOprea, S. O., Garcia-Garcia, A., Orts-Escolano, S., Villena-Martinez, V., and Castro-Vargas, J. A.Expert Systems 2017
A long short-term memory based Schaeffer gesture recognition systemOprea, S. O., Garcia-Garcia, A., Orts-Escolano, S., Villena-Martinez, V., and Castro-Vargas, J. A.Expert Systems 2017In this work, a Schaeffer language recognition system is proposed in order to help autistic children overcome communicative disorders. Using Schaeffer language as a speech and language therapy, improves children communication skills and at the same time the understanding of language productions. Nevertheless, the teaching process of children in performing gestures properly is not straightforward. For this purpose, this system will teach children with autism disorder the correct way to communicate using gestures in combination with speech reproduction. The main purpose is to accelerate the learning process and increase children interest by using a technological approach. Several recurrent neural network-based approaches have been tested, such as vanilla recurrent neural networks, long short-term memory networks, and gated recurrent unit-based models. In order to select the most suitable model, an extensive comparison has been conducted reporting a 93.13% classification success rate over a subset of 25 Schaeffer gestures by using an long short-term memory-based approach. Our dataset consists on pose-based features such as angles and euclidean distances extracted from the raw skeletal data provided by a Kinect v2 sensor.
 A robotic platform for customized and interactive rehabilitation of persons with disabilitiesGomez-Donoso, Francisco, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, Castro-Vargas, John Alejandro, Ovidiu-Oprea, Sergiu, and Cazorla, MiguelPattern Recognition Letters 2017
A robotic platform for customized and interactive rehabilitation of persons with disabilitiesGomez-Donoso, Francisco, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, Castro-Vargas, John Alejandro, Ovidiu-Oprea, Sergiu, and Cazorla, MiguelPattern Recognition Letters 2017In this work, we have developed a multisensor system for rehabilitation and interaction with persons with motor and cognitive disabilities. The system enables them to perform different therapies using multiple modes of interaction (head and body pose, hand gestures, voice, touch and gaze) depending on the type and degree of disability. Through a training process, the system can be customized enabling the definition of patients’ own gestures for each sensor. The system is integrated with a range of applications for rehabilitation. Examples of these applications are puzzle solving, mazes and text writing using predictive text tools. The system also provides a flexible and modular framework for the development of new applications oriented towards novel rehabilitation therapies. The proposed system has been integrated in a mobile robotic platform and uses low-cost sensors allowing to perform non-intrusive rehabilitation therapies at home. Videos showing the proposed system and users interacting in different ways (multimodal) are available on our project website www.rovit.ua.es/patente/.
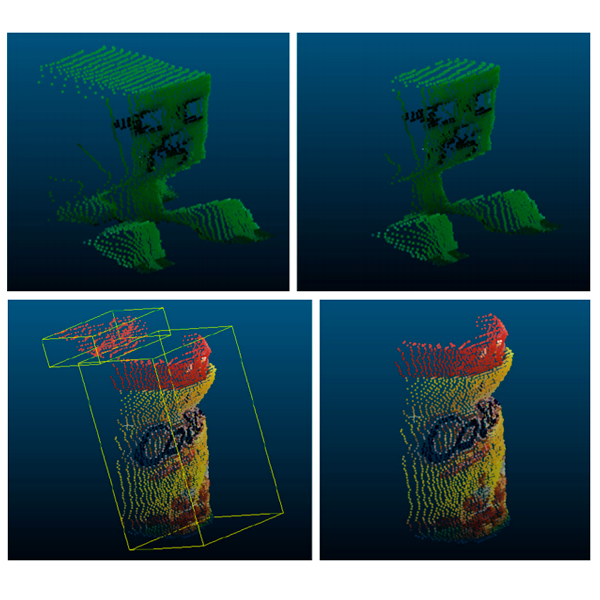 Multi-sensor 3D object dataset for object recognition with full pose estimationGarcia-Garcia, Alberto, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Oprea, Sergiu, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, Azorin-Lopez, Jorge, Saval-Calvo, Marcelo, and Cazorla, MiguelNeural Computing and Applications 2016
Multi-sensor 3D object dataset for object recognition with full pose estimationGarcia-Garcia, Alberto, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Oprea, Sergiu, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, Azorin-Lopez, Jorge, Saval-Calvo, Marcelo, and Cazorla, MiguelNeural Computing and Applications 2016In this work, we propose a new dataset for 3D object recognition using the new high-resolution Kinect V2 sensor and some other popular low-cost devices like PrimeSense Carmine. Since most already existing datasets for 3D object recognition lack some features such as 3D pose information about objects in the scene, per pixel segmentation or level of occlusion, we propose a new one combining all this information in a single dataset that can be used to validate existing and new 3D object recognition algorithms. Moreover, with the advent of the new Kinect V2 sensor we are able to provide high-resolution data for RGB and depth information using a single sensor, whereas other datasets had to combine multiple sensors. In addition, we will also provide semiautomatic segmentation and semantic labels about the different parts of the objects so that the dataset could be used for testing robot grasping and scene labeling systems as well as for object recognition.
conferences
 UnrealROX+: An Improved Tool for Acquiring Synthetic Data from Virtual 3D EnvironmentsMartinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Oprea, Sergiu, Castro-Vargas, John Alejandro, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, and Vincze, MarkusIn 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2021
UnrealROX+: An Improved Tool for Acquiring Synthetic Data from Virtual 3D EnvironmentsMartinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Oprea, Sergiu, Castro-Vargas, John Alejandro, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, and Vincze, MarkusIn 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2021Synthetic data generation has become essential in last years for feeding data-driven algorithms, which surpassed traditional techniques performance in almost every computer vision problem. Gathering and labelling the amount of data needed for these data-hungry models in the real world may become unfeasible and error-prone, while synthetic data give us the possibility of generating huge amounts of data with pixel-perfect annotations. However, most synthetic datasets lack from enough realism in their rendered images. In that context UnrealROX generation tool was presented in 2019, allowing to generate highly realistic data, at high resolutions and framerates, with an efficient pipeline based on Unreal Engine, a cutting-edge videogame engine. UnrealROX enabled robotic vision researchers to generate realistic and visually plausible data with full ground truth for a wide variety of problems such as class and instance semantic segmentation, object detection, depth estimation, visual grasping, and navigation. Nevertheless, its workflow was very tied to generate image sequences from a robotic on-board camera, making hard to generate data for other purposes. In this work, we present UnrealROX+, an improved version of UnrealROX where its decoupled and easy-to-use data acquisition system allows to quickly design and generate data in a much more flexible and customizable way. Moreover, it is packaged as an Unreal plug-in, which makes it more comfortable to use with already existing Unreal projects, and it also includes new features such as generating albedo or a Python API for interacting with the virtual environment from Deep Learning frameworks.
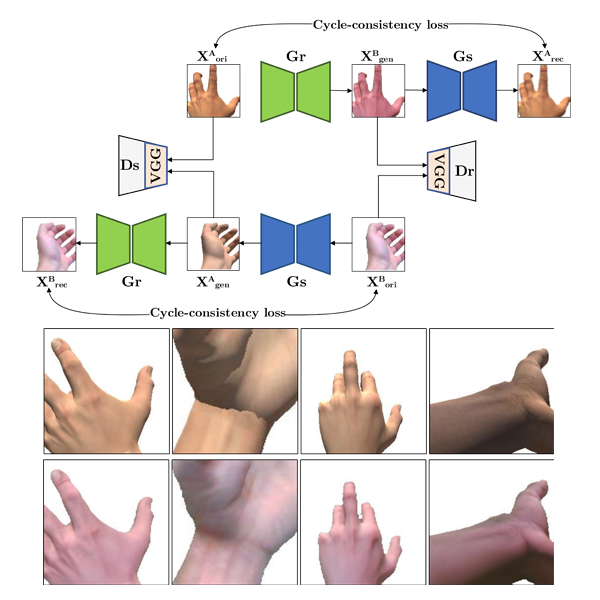 H-GAN: the power of GANs in your HandsOprea, Sergiu, Karvounas, Giorgos, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Kyriazis, Nikolaos, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Oikonomidis, Iason, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Tsoli, Aggeliki, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, and Argyros, AntonisIn 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2021
H-GAN: the power of GANs in your HandsOprea, Sergiu, Karvounas, Giorgos, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Kyriazis, Nikolaos, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Oikonomidis, Iason, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Tsoli, Aggeliki, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, and Argyros, AntonisIn 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2021We present HandGAN (H-GAN), a cycle-consistent adversarial learning approach implementing multi-scale perceptual discriminators. It is designed to translate synthetic images of hands to the real domain. Synthetic hands provide complete ground-truth annotations, yet they are not representative of the target distribution of real-world data. We strive to provide the perfect blend of a realistic hand appearance with synthetic annotations. Relying on image-to-image translation, we improve the appearance of synthetic hands to approximate the statistical distribution underlying a collection of real images of hands. H-GAN tackles not only cross-domain tone mapping but also structural differences in localized areas such as shading discontinuities. Results are evaluated on a qualitative and quantitative basis improving previous works. Furthermore, we successfully apply the generated images to the hand classification task.
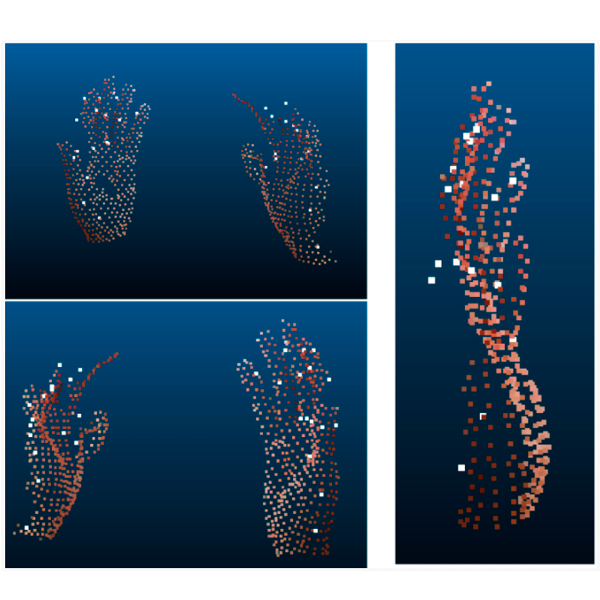 3D Hand Joints Position Estimation with Graph Convolutional Networks: A GraphHands BaselineCastro-Vargas, John-Alejandro, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Oprea, Sergiu, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, and Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose2019
3D Hand Joints Position Estimation with Graph Convolutional Networks: A GraphHands BaselineCastro-Vargas, John-Alejandro, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Oprea, Sergiu, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, and Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose2019State-of-the-art deep learning-based models used to address hand challenges, e.g. 3D hand joint estimation, need a vast amount of annotated data to achieve a good performance. The lack of data is a problem of paramount importance. Consequently, the use of synthetic datasets for training deep learning models is a trend and represents a promising avenue to improve existing approaches. Nevertheless, currently existing synthetic datasets lack of accurate and complete annotations, realism, and also rich hand-object interactions. For this purpose, in our work we present a synthetic dataset featuring rich hand-object interactions in photorealistic scenarios. The applications of our dataset for hand-related challenges are unlimited. To validate our data, we propose an initial approach to 3D hand joint estimation using a graph convolutional network feeded with point cloud data. Another point in favour of our dataset is that interactions are performed using realistic objects extracted from the YCB dataset. This could allow to test trained systems with our synthetic dataset using images/videos manipulating the same objects in real life.
 The RobotriX: An Extremely Photorealistic and Very-Large-Scale Indoor Dataset of Sequences with Robot Trajectories and InteractionsGarcia-Garcia, Alberto, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Oprea, Sergiu, Castro-Vargas, John Alejandro, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, and Jover-Alvarez, AlvaroIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2018 Also at 3D Scene Generation workshop (CVPR 2019).
The RobotriX: An Extremely Photorealistic and Very-Large-Scale Indoor Dataset of Sequences with Robot Trajectories and InteractionsGarcia-Garcia, Alberto, Martinez-Gonzalez, Pablo, Oprea, Sergiu, Castro-Vargas, John Alejandro, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose, and Jover-Alvarez, AlvaroIn IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2018 Also at 3D Scene Generation workshop (CVPR 2019).Enter the RobotriX, an extremely photorealistic indoor dataset designed to enable the application of deep learning techniques to a wide variety of robotic vision problems. The RobotriX consists of hyperrealistic indoor scenes which are explored by robot agents which also interact with objects in a visually realistic manner in that simulated world. Photorealistic scenes and robots are rendered by Unreal Engine into a virtual reality headset which captures gaze so that a human operator can move the robot and use controllers for the robotic hands; scene information is dumped on a per-frame basis so that it can be reproduced offline using UnrealCV to generate raw data and ground truth labels. By taking this approach, we were able to generate a dataset of 38 semantic classes across 512 sequences totaling 8M stills recorded at +60 frames per second with full HD resolution. For each frame, RGB-D and 3D information is provided with full annotations in both spaces. Thanks to the high quality and quantity of both raw information and annotations, the RobotriX will serve as a new milestone for investigating 2D and 3D robotic vision tasks with large-scale data-driven techniques.
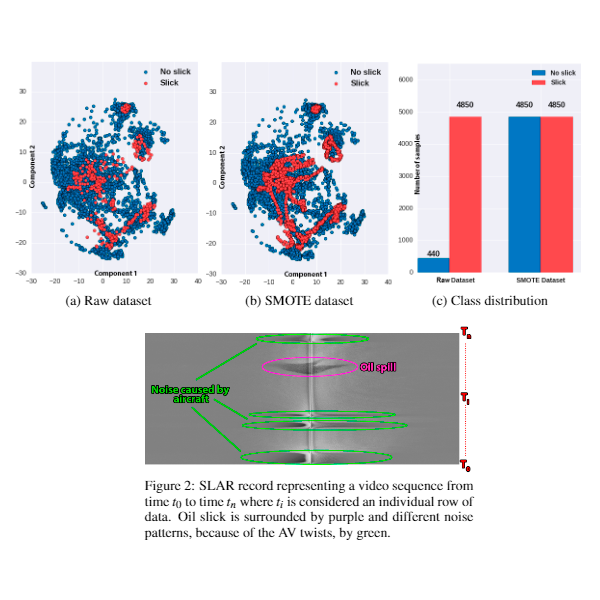 Candidate Oil Spill Detection in SLAR Data - A Recurrent Neural Network-based ApproachOprea, Sergiu-Ovidiu, Gil, Pablo, Mira, Damian, and Alacid, BeatrizIn Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods 2017
Candidate Oil Spill Detection in SLAR Data - A Recurrent Neural Network-based ApproachOprea, Sergiu-Ovidiu, Gil, Pablo, Mira, Damian, and Alacid, BeatrizIn Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods 2017Intentional oil pollution damages marine ecosystems. Therefore, society and governments require maritime surveillance for early oil spill detection. The fast response in the detection process helps to identify the offenders in the vast majority of cases. Nowadays, it is a human operator whom is trained for carrying out oil spill detection. Operators usually use image processing techniques and data analysis from optical, thermal or radar acquired from aerial vehicles or spatial satellites. The current trend is to automate the oil spill detection process so that this can filter candidate oil spill from an aircraft as a decision support system for human operators. In this work, a robust and automated system for candidate oil spill based on Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) is presented. The aim is to provide a faster identification of the candidate oil spills from SLAR scanned sequences. So far, the majority of the research works about oil spill detection are focused on the classification between real oil spills and look-alikes, and they use SAR or optical images but not SLAR. Furthermore, the overall decision is usually taken by an operator in the research works of state-of-art, mainly due to the wide variety of types of look-alikes which cause false positives in the detection process when traditional NN are used. This work provides a RRN-based approach for candidate oil spill detection using SLAR data in contrast with the traditional Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network (MPNN). The system is tested with temporary data acquired from a SLAR sensor mounted on an aircraft. It achieves a success rate in detecting of 97%.
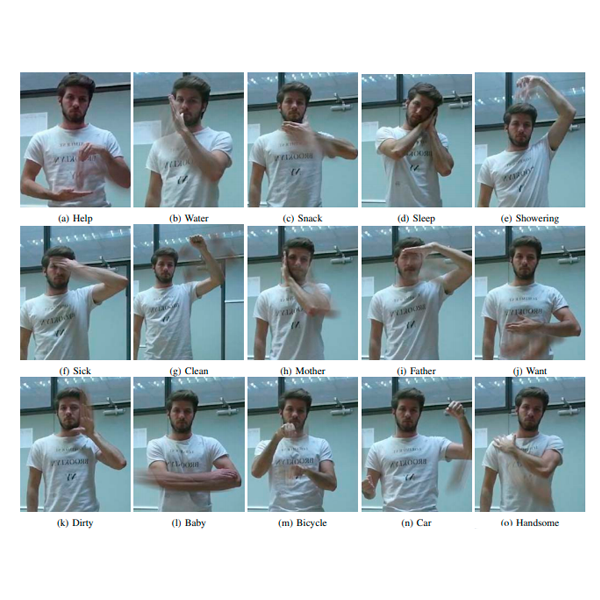 A recurrent neural network based Schaeffer gesture recognition systemOprea, S., Garcia-Garcia, A., Garcia-Rodriguez, J., Orts-Escolano, S., and Cazorla, M.In 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2017
A recurrent neural network based Schaeffer gesture recognition systemOprea, S., Garcia-Garcia, A., Garcia-Rodriguez, J., Orts-Escolano, S., and Cazorla, M.In 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2017Schaeffer language is considered an effective method to help autistic children overcome communicative disorders. Speech and language therapy results in an improvement in communication skills and understanding of language productions. In this work, a Schaeffer language recognition system is presented with the purpose of teaching children with autism disorder the correct way to communicate using gestures in combination with speech reproduction. The purpose is to accelerate the learning process and increase children interest using a technological approach. A Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model has been implemented for this purpose reporting a 93.13% classification success rate over a subset of 25 Schaeffer gestures. A comparison with vanilla RNNs and GRU-based models has been also carried out. Pose-based features such as angles and euclidean distances have been extracted from our gesture dataset by processing raw skeletal data from a Kinect v2 sensor.
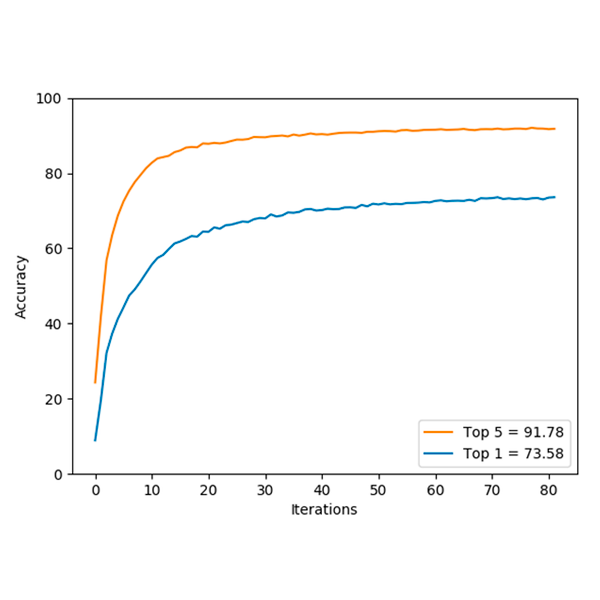 Classifying Behaviours in Videos with Recurrent Neural NetworksAbellan-Abenza, Javier, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Oprea, Sergiu, Ivorra-Piqueres, David, and Garcia-Rodriguez, JoseInternational Journal of Computer Vision and Image Processing 2017
Classifying Behaviours in Videos with Recurrent Neural NetworksAbellan-Abenza, Javier, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Oprea, Sergiu, Ivorra-Piqueres, David, and Garcia-Rodriguez, JoseInternational Journal of Computer Vision and Image Processing 2017This article describes how the human activity recognition in videos is a very attractive topic among researchers due to vast possible applications. This article considers the analysis of behaviors and activities in videos obtained with low-cost RGB cameras. To do this, a system is developed where a video is input, and produces as output the possible activities happening in the video. This information could be used in many applications such as video surveillance, disabled person assistance, as a home assistant, employee monitoring, etc. The developed system makes use of the successful techniques of Deep Learning. In particular, convolutional neural networks are used to detect features in the video images, meanwhile Recurrent Neural Networks are used to analyze these features and predict the possible activity in the video.
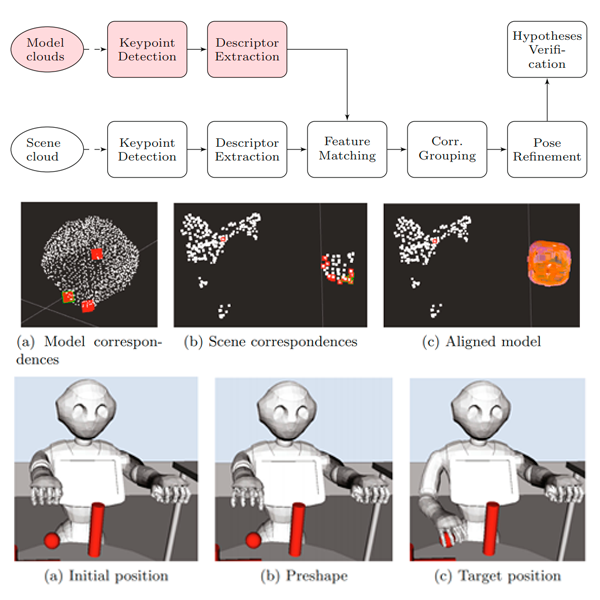 Detecting and Manipulating Objects with a Social Robot: An Ambient Assisted Living ApproachCastro-Vargas, John Alejandro, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Oprea, Sergiu, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, and Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose2017
Detecting and Manipulating Objects with a Social Robot: An Ambient Assisted Living ApproachCastro-Vargas, John Alejandro, Garcia-Garcia, Alberto, Oprea, Sergiu, Orts-Escolano, Sergio, and Garcia-Rodriguez, Jose2017Object grasping in domestic environments using social robots has an enormous potential to help dependant people with certain degree of disability. In this work, we made use of the well-known Pepper social robot to carry out such task. We provide an integrated solution using ROS to recognize and grasp simple objects. That system was deployed on an accelerator platform (Jetson TX1) to be able to perform object recognition in real time using RGB-D sensors attached to the robot. By using our system, we proved that the Pepper robot shows a great potential for such kind of domestic assistance tasks.
book chapters
 Object Recognition PipelineVargas, John Alejandro Castro, Garcia, Alberto Garcia, Oprea, Sergiu, Escolano, Sergio Orts, and Rodriguez, Jose Garcia2019
Object Recognition PipelineVargas, John Alejandro Castro, Garcia, Alberto Garcia, Oprea, Sergiu, Escolano, Sergio Orts, and Rodriguez, Jose Garcia2019Object grasping in domestic environments using social robots has an enormous potential to help dependent people with a certain degree of disability. In this chapter, the authors make use of the well-known Pepper social robot to carry out such task. They provide an integrated solution using ROS to recognize and grasp simple objects. That system was deployed on an accelerator platform (Jetson TX1) to be able to perform object recognition in real time using RGB-D sensors attached to the robot. By using the system, the authors prove that the Pepper robot shows a great potential for such domestic assistance tasks.